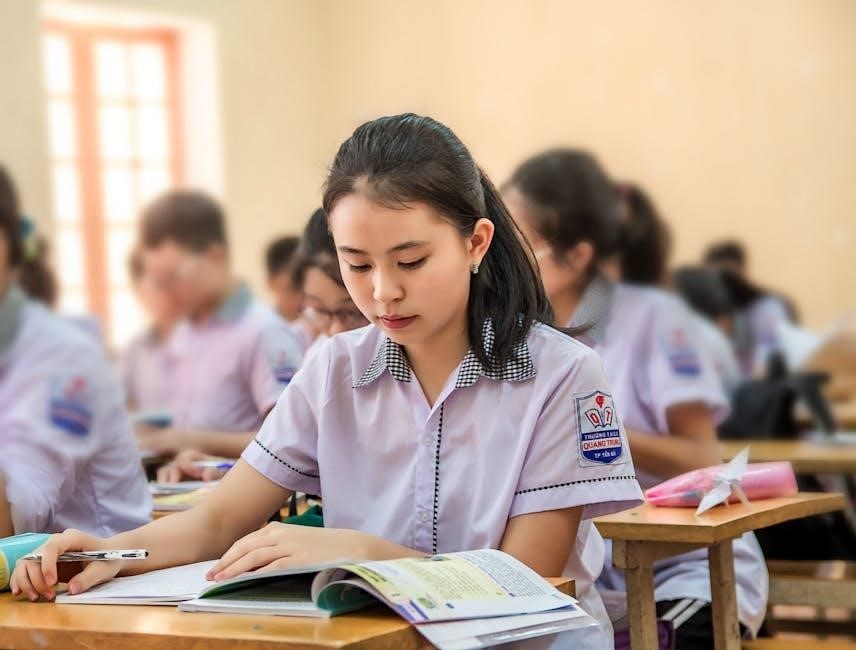
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana, a National Book Award finalist and New York Times bestseller, explores cultural identity and family expectations through Julia’s story, contrasting her ambitions with her sister Olga’s traditional role, delving into themes of belonging and self-discovery.
1.1 Overview of the Book
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana, written by Erika L. Sánchez, is a poignant coming-of-age story about Julia, a young Mexican-American girl navigating cultural expectations, family dynamics, and personal identity. The novel, a National Book Award finalist and New York Times bestseller, explores themes of belonging, rebellion, and self-discovery. Set in Chicago, the book delves into Julia’s struggles with her parents’ traditional values and her desire to forge her own path. The narrative offers a raw, emotional portrayal of the immigrant experience and the challenges of balancing heritage with individual aspirations. Available in PDF, EPUB, and Kindle, the book resonates deeply with readers grappling with identity and cultural pressures.
1.2 The Author: Erika L. Sánchez
Erika L. Sánchez, a Mexican-American poet and writer, gained acclaim with her debut novel Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana. A National Book Award finalist and recipient of the 21st Century Award from the Chicago Public Library Foundation, Sánchez explores themes of identity, culture, and family. Her work resonates with readers navigating cultural duality, blending raw emotion with vivid storytelling. A fellow of the National Endowment for the Arts, Sánchez’s writing reflects her deep connection to her heritage and her ability to articulate the immigrant experience. Her voice has become a vital contribution to Latino literature.
1.3 Cultural Context and Significance
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana holds profound cultural significance, offering a raw portrayal of the Mexican-American experience. It challenges stereotypes and explores themes of identity, family expectations, and the immigrant journey. The novel resonates deeply with readers who navigate cultural duality, providing a voice to underrepresented communities. By addressing generational conflicts and societal pressures, Sánchez’s work bridges gaps between traditional Mexican values and modern American life. Its impact lies in its ability to spark conversations about belonging, heritage, and resilience, making it a vital contribution to contemporary Latino literature and a reflection of the broader immigrant experience.

Main Characters and Their Roles
Julia, the protagonist, rebels against traditional expectations, while her sister Olga embodies the ideal Mexican daughter. Their parents struggle with cultural expectations and personal loss, shaping the family dynamics.
2.1 Julia: The Protagonist
Julia is a determined and ambitious teenager who rejects the traditional role expected of her as a Mexican daughter. She aspires to attend college and pursue a career, unlike her sister Olga, who stayed home to care for their parents. Julia’s journey is marked by her desire for independence and self-discovery, often leading to conflicts with her family. Her strong will and rebellious nature drive the story, as she navigates cultural expectations, personal identity, and the complexities of her family’s struggles. Julia’s character embodies the tension between tradition and modern aspirations.
2.2 Olga: The “Perfect” Mexican Daughter
Olga represents the ideal of a traditional Mexican daughter, fulfilling her parents’ expectations by staying at home, caring for them, and managing household responsibilities. She embodies the cultural norms of loyalty and sacrifice, contrasting sharply with Julia’s rebellious aspirations. Olga’s role highlights the pressures placed on women in Latino culture to prioritize family over personal ambitions, creating tension with Julia, who seeks independence and a different future. This dynamic underscores the cultural conflicts and generational divides central to the story, making Olga a pivotal figure in exploring themes of identity and tradition. Her presence shapes Julia’s journey, emphasizing the sacrifices expected of daughters in preserving family heritage.
2.3 The Parents: Their Expectations and Struggles
The parents in Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana embody traditional Mexican values, expecting their daughters to prioritize family and cultural norms. They envision Julia following in Olga’s footsteps, caring for the household and sacrificing personal goals for familial loyalty. Their struggles stem from balancing cultural identity with their daughters’ modern aspirations, leading to generational and cultural conflicts. The parents’ rigid expectations reflect their own sacrifices as immigrants, creating tension as Julia rebels against their ideals. This dynamic highlights the challenges of preserving heritage while navigating contemporary realities, making their struggles central to the story’s emotional core.

Themes Explored in the Book
The novel explores identity, family expectations, grief, rebellion, and the immigrant experience, offering a powerful exploration of cultural and personal struggles through Julia’s journey.
3.1 Identity and Belonging
Julia grapples with her dual identity, caught between her Mexican heritage and American surroundings. She feels suffocated by her parents’ traditional expectations, longing for autonomy and self-expression. Her journey reflects the struggle of many Latino youth to balance cultural loyalty with personal aspirations. The novel poignantly captures the tension between belonging to a family and forging one’s own path, highlighting the challenges of navigating cultural and generational gaps. Through Julia’s story, Sánchez offers a powerful exploration of identity, resilience, and the quest to find one’s place in the world.
3.2 Family Expectations and Cultural Pressures
In Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana, family expectations and cultural pressures are central to Julia’s struggle; Her parents envision a traditional path for their daughters, with Olga embodying the role of the obedient, stay-at-home daughter. Julia, however, rebels against these constraints, yearning for college and independence. The novel vividly portrays the tension between cultural duty and personal ambition, highlighting the suffocating weight of familial and societal expectations. Through Julia’s experiences, Sánchez illuminates the challenges of navigating traditional values in a modern world, where individual desires often clash with cultural obligations.
3.3 Grief and Loss
Grief and loss are profound themes in Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana, particularly following the death of Julia’s sister, Olga. The tragedy reshapes family dynamics, intensifying Julia’s internal conflict and her strained relationship with her parents. The novel delves into the emotional toll of loss, exploring how grief manifests differently across generations and cultures. Julia’s journey is marked by guilt, sadness, and self-discovery, as she grapples with the expectations tied to her sister’s memory. Sánchez’s portrayal of loss highlights its universality, transcending cultural boundaries to resonate deeply with readers.
3.4 Rebellion and Self-Discovery
Julia’s rebellion against her family’s traditional expectations drives her journey of self-discovery. She challenges the limitations imposed by her parents, seeking independence and a future beyond the confines of cultural norms. Through her defiance, Julia explores her identity, balancing her Mexican heritage with her American experiences. Her rebellion is not just against her family but also against societal expectations, as she strives to carve her own path. This internal and external conflict fuels her growth, as she navigates guilt, fear, and the pursuit of her ambitions, ultimately finding a sense of self that honors both her roots and her aspirations.
3.5 The Immigrant Experience
The immigrant experience is central to the novel, as Julia’s family navigates the complexities of preserving their Mexican heritage while adapting to life in America. The sacrifices and unspoken struggles of the parents, who left Mexico for a better future, are poignantly portrayed. Their expectations, rooted in cultural traditions, often clash with Julia’s desire for independence and self-expression. The book highlights the tension between maintaining cultural identity and embracing a new life, as well as the pressure to honor one’s roots while forging a path in a different world. This duality resonates deeply in Julia’s journey of self-discovery and rebellion.

Plot Structure and Key Events
The story unfolds in Chicago, blending Mexican heritage with American life. Julia’s journey is sparked by a pivotal incident, narrated with raw, emotional depth and clarity.
4.1 The Setting: Chicago and Mexican Heritage
The story is set in Chicago, where the protagonist, Julia, navigates her identity between her Mexican heritage and American surroundings. The city’s vibrant, diverse neighborhoods serve as a backdrop for her journey, reflecting the cultural duality she experiences. The setting highlights the contrast between the traditional expectations of her Mexican household and the broader American culture she encounters. This duality shapes her struggles and aspirations, making Chicago a character in itself, influencing her growth and self-discovery. The interplay between her home life and the city’s multicultural environment underscores the themes of identity and belonging.
4.2 The Narrative Style and Voice
The novel is written in a raw, unflinching first-person narrative, offering an intimate glimpse into Julia’s thoughts and emotions. Her sharp, often sarcastic voice captures the complexity of her identity and the tensions between her ambitions and cultural expectations. The present-tense storytelling creates immediacy, drawing readers into her world. The narrative seamlessly blends humor and heartache, reflecting Julia’s resilience and vulnerability. This direct, unfiltered voice makes her relatable and authentic, allowing readers to deeply connect with her journey of self-discovery and growth amidst familial and cultural pressures.
4.3 The Incident That Changes Everything
The death of Julia’s sister, Olga, is the pivotal event that reshapes her world. Olga, the embodiment of the “perfect Mexican daughter,” dies unexpectedly, leaving a void that exposes the cracks in the family’s dynamics. This tragedy forces Julia to confront her parents’ expectations and cultural pressures, while also grappling with her own guilt and grief. The incident sparks Julia’s journey of self-discovery, as she begins to question her identity and the path laid out for her. It also reveals hidden truths about Olga’s life, challenging Julia’s perceptions of her sister and their family’s traditions.
4.4 Julia’s Journey of Self-Discovery
Julia’s journey of self-discovery is marked by her struggle to reconcile her ambitions with her family’s expectations. As she navigates her identity, she grapples with cultural pressures and her own guilt over wanting more than the traditional role set for her. Her relationship with her parents becomes strained, yet she finds solace in her passion for poetry and education. Through her experiences, Julia learns to embrace her individuality, challenging the norms imposed by her family and society. This journey is pivotal in her growth, as she seeks to find her place in the world while staying true to herself.
4.5 The Climax and Resolution
The climax of the story unfolds as Julia confronts her family about her aspirations and the suffocating expectations placed upon her. A tragic event involving her sister Olga forces Julia to reckon with grief, guilt, and the reality of her choices. In the resolution, Julia begins to heal and find a sense of peace, learning to balance her desire for independence with her love for her family. The novel concludes with Julia embracing her identity and pursuing her dreams, showing growth and a newfound understanding of herself and her heritage.
Reception and Reviews
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana received widespread acclaim, becoming a National Book Award finalist and a New York Times bestseller. Its raw portrayal of cultural identity resonated deeply with readers, making it a celebrated work in Latino literature and a staple in many book clubs and school curriculums.
5.1 Critical Acclaim and Awards
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana garnered significant critical acclaim, becoming a finalist for the prestigious National Book Award and earning a spot on the New York Times bestseller list. Critics praised its raw, emotional storytelling and its unflinching exploration of cultural identity, family dynamics, and personal struggle. The book also received the 21st Century Award from the Chicago Public Library Foundation and was recognized for its authentic portrayal of the immigrant experience. Its success solidified Erika L. Sánchez’s place as a prominent voice in contemporary Latino literature, resonating with readers and critics alike.
5.2 Commercial Success and Bestseller Status
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana achieved remarkable commercial success, debuting as a New York Times bestseller and maintaining its position due to its resonant storytelling. The book’s popularity soared upon its release in 2017, attracting a wide audience with its relatable themes of identity and family. Its availability in formats like PDF, EPUB, and Kindle further boosted accessibility, making it a favorite among young adult readers and book clubs. The novel’s cultural relevance and emotional depth have cemented its status as a modern classic in Latino literature, driving its enduring popularity and critical acclaim.
5.3 Reader Responses and Impact
Readers have deeply connected with Julia’s journey, praising the book’s honest portrayal of cultural identity and family dynamics. The novel has sparked meaningful discussions in book clubs and classrooms, resonating particularly with young Latino readers who see themselves in Julia’s struggles. Critics and audiences alike have celebrated its raw authenticity and emotional depth. Its relatable themes have made it a cherished and impactful read, fostering empathy and understanding. The book’s ability to address universal and personal challenges has left a lasting impression, solidifying its place in contemporary young adult literature.
The PDF Version and Its Popularity
The PDF version of Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana is widely available, offering readers accessible formats like EPUB and Kindle, enhancing its popularity among diverse audiences.
6.1 Availability and Accessibility
The PDF version of Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana is widely accessible, available for download in formats like PDF, EPUB, and Kindle. Published by VINTAGE ESPAÑOL in 2018, the book spans 269 pages, making it easily shareable and readable across devices. Its digital availability has contributed to its popularity, allowing readers worldwide to engage with Julia’s powerful story. The PDF format ensures compatibility with various platforms, enhancing its reach and convenience for audiences seeking to explore themes of identity and culture in a modern, portable format.
6.2 Reasons for the PDF’s Popularity
The PDF version of Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana gained popularity due to its convenience and accessibility. Readers appreciate the ability to access the story on multiple devices, making it easy to read anywhere. The digital format also appeals to younger audiences familiar with e-books. Additionally, the book’s themes of identity, culture, and family resonate widely, attracting a diverse readership. Its status as a bestseller and National Book Award finalist further boosted its popularity, driving demand for the PDF version as a preferred way to experience Julia’s compelling journey of self-discovery and cultural exploration.
6.3 Legal and Ethical Considerations
The PDF version of Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana raises legal and ethical concerns. Copyright laws protect the book, and unauthorized distribution or downloading violates these protections. Publishers use DRM (Digital Rights Management) to prevent illegal sharing, ensuring authors and creators receive fair compensation. Ethically, readers are encouraged to support the author and publisher by purchasing legitimate copies, promoting the sustainability of literary work. Piracy undermines the industry and the ability to produce diverse, impactful stories like Julia’s, which resonate deeply with its audience and contribute to cultural representation in literature.
Adaptations and Spin-Offs
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana has sparked interest in film and stage adaptations, with its emotional depth and cultural relevance making it ideal for visual storytelling.
7.1 Potential Film Adaptation
The emotional depth and cultural relevance of Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana make it a strong candidate for a film adaptation. Its exploration of identity, family, and societal expectations could resonate powerfully on screen. The story’s vivid characters, particularly Julia’s journey, offer rich material for cinematic storytelling. While no official adaptation has been announced, the book’s success and themes suggest it could thrive in a film format, appealing to a broad audience interested in coming-of-age narratives and Latino experiences. Its visual potential and universal themes make it an attractive option for filmmakers.
7.2 Stage Play Possibilities
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana could be adapted into a compelling stage play, leveraging its emotional depth and strong character dynamics. The story’s focus on family, identity, and cultural clashes would translate well into a theatrical format. The dialogue-driven narrative and vivid settings, such as Julia’s home and Chicago’s Latino community, could be brought to life through minimalist yet evocative stage designs. The play could highlight Julia’s internal struggles and her relationships, resonating with audiences seeking stories about self-discovery and cultural identity. Its themes of rebellion and belonging would particularly appeal to young Latino audiences.
7.3 Sequel or Related Works
There is currently no official sequel to Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana, but the book’s success has sparked discussions about potential spin-offs or related works. Fans have expressed interest in exploring Julia’s journey beyond the novel, particularly her experiences in college or her return to her roots. Erika L. Sánchez has also written other works, such as Crying in the Bathroom, which touches on similar themes of identity and culture. A sequel or spin-off could delve into supporting characters like Olga or expand on the family’s history, offering deeper insights into their world.

The Book’s Impact on Latino Literature
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana has become a landmark in Latino literature, offering an authentic voice to the experiences of Mexican-American youth and inspiring new writers to explore cultural identity and family dynamics with raw honesty and depth.
8.1 Representation in Literature
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana fills a critical gap in Latino literature by offering a raw, unfiltered portrayal of the Mexican-American experience, particularly for young women. The novel challenges stereotypes by presenting complex, multi-dimensional characters like Julia, who embody the struggles of cultural identity and generational divides. By voicing the experiences of marginalized communities, the book provides a platform for underrepresented stories, fostering a deeper understanding of Latino culture. Its authenticity resonates with readers, inspiring a new wave of storytelling that celebrates diversity and challenges societal expectations.
8.2 Breaking Stereotypes
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana challenges stereotypes surrounding the Mexican-American experience by presenting a nuanced portrayal of identity, family, and culture. Julia’s defiance of traditional roles and her pursuit of personal ambitions contradict the expectation of the “perfect Mexican daughter.” The novel dismantles the notion of a monolithic Latino identity, offering instead a complex exploration of individuality and generational conflict. By rejecting simplistic portrayals, the book humanizes characters like Julia, who embodies both resilience and imperfection. This authentic representation helps break down cultural and societal stereotypes, offering readers a more realistic understanding of the Latino experience.
8.4 Inspiring Young Latino Writers
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana has become a powerful inspiration for young Latino writers, offering a relatable and authentic voice that resonates deeply with their experiences. Erika L. Sánchez’s unflinching portrayal of identity, culture, and family challenges has encouraged many to embrace their own stories. The novel’s success demonstrates the importance of diverse narratives, motivating young writers to explore their heritage and personal struggles. By breaking cultural silences, the book empowers a new generation to express themselves freely, fostering a sense of pride and ownership over their unique experiences. This has made it a cornerstone of inspiration for emerging Latino voices.
Educational Use and Discussions
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana is widely used in schools and universities for its rich themes of identity, culture, and family, sparking meaningful classroom discussions and reflections.
9.1 Use in Schools and Universities
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana is increasingly incorporated into school and university curricula for its exploration of identity, culture, and family dynamics. The book’s themes resonate deeply with students, particularly those navigating multicultural experiences. Educators use it to foster discussions on belonging, expectations, and self-discovery. Its accessible language and relatable protagonist make it an ideal choice for literature and diversity-focused classes. The PDF version’s availability further enhances its adoption in educational settings, allowing easy access for students and educators alike.
9.2 Discussion Topics for Book Clubs
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana offers rich material for book clubs, sparking conversations on identity, cultural expectations, and family dynamics. Key topics include Julia’s struggle with her parents’ traditional values, the contrast between her and Olga’s paths, and the impact of grief on the family. The book also invites discussions on self-discovery, rebellion, and the immigrant experience. The PDF version’s accessibility makes it easy for clubs to reference key passages. Questions about cultural identity, personal aspirations, and societal pressures further deepen the exploration of Julia’s journey and its relevance to readers’ lives.
9.3 Teaching the Book in Classrooms
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana is a valuable addition to classroom curricula, offering insights into identity, culture, and family dynamics. Educators can use the book to explore themes of belonging, rebellion, and the immigrant experience, aligning with diverse curriculum standards. The narrative’s emotional depth and relatable protagonist make it ideal for sparking discussions on cultural identity and personal aspirations. The PDF version’s accessibility allows teachers to easily assign and reference key passages, facilitating analysis and critical thinking. It also encourages students to reflect on societal expectations and their own experiences, fostering empathy and understanding.
The Role of Social Media in Popularizing the Book
Social media platforms like Instagram and TikTok amplified the book’s reach, with users sharing quotes and reviews, fostering online discussions and connecting readers globally.
10.1 Bookstagram and Online Communities
Bookstagram and online communities played a pivotal role in popularizing Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana. Users shared heartfelt reviews, quotes, and personal connections to Julia’s journey, resonating deeply with Latino readers. The book’s themes of identity and cultural pressures sparked widespread discussions, with hashtags like #Latinx Literature and #BookRecommendations amplifying its reach. Online forums and social media groups dedicated to diverse reads further highlighted its impact, creating a digital buzz that attracted new readers and solidified its place in contemporary young adult literature.
10.2 Reviews and Recommendations
Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana has garnered widespread critical acclaim and reader admiration. Reviewers praise its raw portrayal of cultural identity, family dynamics, and personal resilience. The book’s emotional depth and relatable protagonist, Julia, have resonated with many, making it a favorite among young adult readers. Recommendations from book bloggers, educators, and reading communities have further boosted its popularity. Its availability in PDF format has also made it easily accessible, contributing to its widespread readership and enthusiastic endorsements across literary circles and social media platforms.
10.3 The Author’s Online Presence
Erika L. Sánchez’s strong online presence has significantly contributed to the book’s popularity. She actively engages with readers on platforms like Twitter and Instagram, sharing insights into her writing process and personal experiences. Her relatable voice and advocacy for Latino literature resonate deeply with her audience. The availability of Yo No Soy Tu Perfecta Hija Mexicana in PDF format has also been promoted through her social media channels, reaching a broader audience and fostering a loyal fan base. Her online interactions have not only boosted the book’s visibility but also created a community around her work.